Mapping functionality is an integral part of almost every type of logistics software. For instance, route planning in a transport management system and real-time tracking in a customer portal rely heavily on maps. The right choice of mapping tool can cut your operating costs and help you build transparent relationships with your customers. But what tool should you choose?
Google Maps is the first worldwide mapping service that comes to mind. It’s a trusted and easy-to-integrate solution that offers a wide range of services to ease the lives of logistics managers.
Read also: How to Use Technologies in Logistics Management System Development
However, in July 2018, Google introduced a new pricing structure for companies using Google Maps APIs. The prices soared, while the number of free API calls was greatly reduced. For instance, users could previously initiate 25,000 Dynamic Maps loads per day for free. Now, the limit is 28,000 per month. Google also started to require all API calls to use a valid API key, which has to be linked to a Google Cloud Platform account.
Small companies aren’t likely to reach the new limit. But when the number of customers and everyday freight traffic grows, the price for Google Maps services grows significantly. So what can you do to cut costs? Are there any Google Maps alternatives? We wanted to figure out if Mapbox is a worthy Google Maps replacement given the high cost of Google Maps. Before we dive into our findings, let’s begin with explaining what Mapbox is.
What is Mapbox?
Mapbox is one of the largest providers of custom designed maps for websites and mobile apps. This service is used by well-known delivery and transportation companies like DHL, DPDgroup, Grubhub, Instacart.
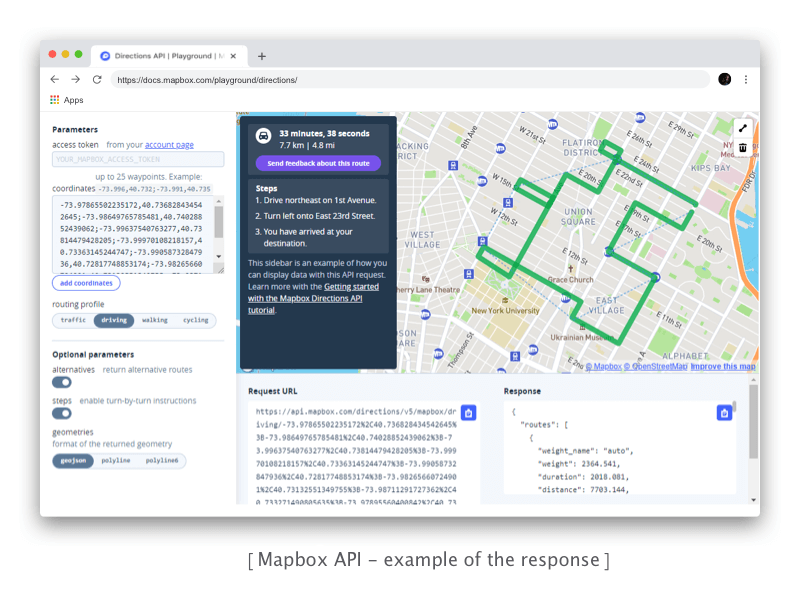
The majority of data Mapbox uses is openly available, and Mapbox supports a community of volunteer mappers. They often provide the freshest updates, including fast-changing location data. Mapbox data sources include OpenStreetMap (OSM), USGS, Landsat, Natural Earth, and OpenAddresses.
The platform uses OpenStreetMap as the base map and lets developers add different markers, lines, polylines, and polygons as well as layers from external sources (in GeoJSON, GPX, and other formats).
Mapbox technology is based on the Node.js language, Mapnik (an open-source toolkit for rendering maps), GDAL (a translator library for raster and vector geospatial data formats), and Leaflet (a JavaScript library for interactive maps).
If you're seeking privacy-friendly alternatives to Google Maps, check out how to use Mapbox securely.
Mapbox offers many tools to help you integrate maps and other Mapbox online web mapping services – such as Directions, Geocoding, and Static Images – into a mobile app. In order to keep the Maps SDKs for iOS and Android small, Mapbox provides different mapping APIs for interfacing with Mapbox web services: the Mapbox Directions API, Geocoding API, and Static Images API.
What do Google Maps and Mapbox have in common?
Google Maps and Mapbox share lots of features. Let’s take a look at some similarities between these tools:
-
Extremely customizable interfaces. Both services offer visual editors for styling. However, you’ll have to use some technical approaches to implement them. Check out how to create a custom style with Google Maps here and with Mapbox here.
-
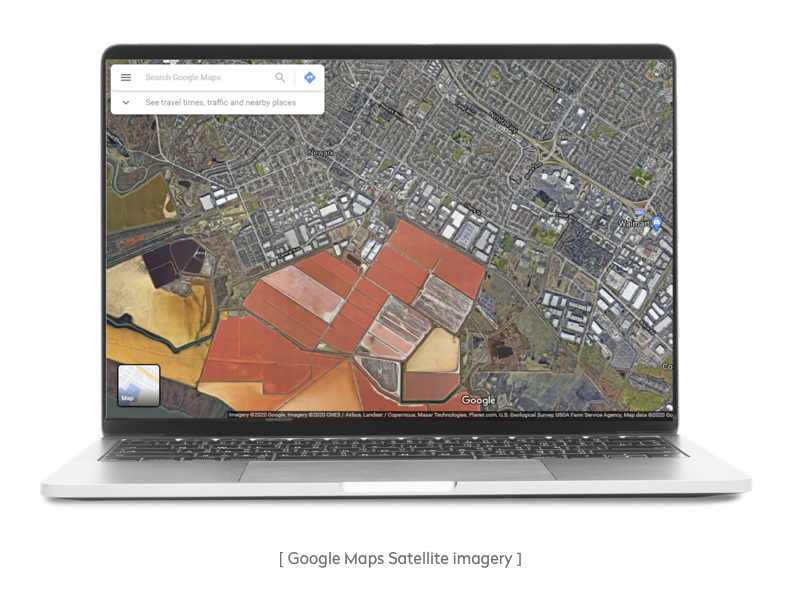
Satellite imagery. Google has some advantages on this front, but they’re barely perceptible. At the moment, Mapbox Satellite is a global base map playing the role of a blank canvas or an overlay for your own data. Mapbox Satellite Streets aggregates Mapbox Satellite data with vector data from Mapbox Streets, which is an all-round set of road, label, and POI data.
-
Search functionality. Auto-suggest is built into the JavaScript APIs of both Google Maps and Mapbox. Both location platforms provide map software solutions to search for places and specific parameters including type of business. As for Mapbox, its autocomplete suggestions and complex search algorithm help to retrieve relevant results even with misspellings.
-
Rich tools for route planning. Both Google and Mapbox have advanced functionality for route planning that you can implement in your software. In one of our past articles, we talked in detail about route planning solutions and described Google Maps and Mapbox, as well as related products. We recommend reading it if you want to learn more about the route planning capabilities these tools offer.
Pros & cons of using Google Maps
Google Maps is a Google map-related product which is based on trustworthy navigation data and has over one billion monthly active users, making this service the most popular. Let’s pay attention to its main pros and cons:
Pros
-
The best information. Thanks to Google’s satellites, Street View vehicles, and user-generated corrections, Google’s geographical coverage is considered the best.
-
Multiple style options. The JSON-like syntax used by Google Maps is immediately loaded along with a map. You can manage the visibility, color, and opacity of all map elements.
-
Street View. Street View is a feature that provides interactive panoramas from different positions along lots of streets around the world. This feature can visualize Keyhole Markup Language (KML) and GeoRSS data on the map. For example, KML syntax tells Google Maps how to display geographic features such as places of interest, images, polygons, etc., and can provide everything from crime statistics to information about recent earthquakes. By integrating the Street View feature into a mobile or web-based version of their apps, restaurants, stores, and other service providers can let customers virtually visit their locations.
-
Extensive language support. Google Maps supports many languages. In 2018, Google added 39 new languages, including Swedish and Armenian, to the Google Maps software, allowing an additional estimated 1.25 billion individuals to use the service in their native language.
Cons
Browser limitations. The Google Maps JavaScript API doesn’t support all web browsers. Jump to the link here to find out which browsers are supported.
Usage limitations. Google Maps limits the number of queries you can make to Google Maps Platform products per second. The table with limitations could be found on Google Maps website. For instance, you can send 50 queries to Directions API. You have to constantly monitor your API usage to check expenditures, and if you exceed the limits, your account will be blocked.
Tricky pricing. The Google Maps pricing model is not easy to sort out. This is the biggest catch: To attract users, Google gives each user $200 in monthly credit for API calls. When this amount is used up, Google begins to charge. This $200 will cover:
– Up to 28,000 Dynamic Maps loads
– Up to 100,000 Static Maps loads
– Up to 40,000 Directions calls
– Up to 40,000 Geolocation calls
Seems like a great deal, right? But in fact, it’s not. Let’s say you use the Embed API in Directions, Views, and Search mode. That’s when your Google Maps service costs begin to skyrocket. If your service loads a map along with initiating an address search using autocomplete and provides geolocation services for directions or distances, that’s three separate API calls for one page load:
1. Autocomplete makes a call for all letters typed in the search bar
2. Another API call is made when a location is selected
3. The API call adds directions to the nearest location
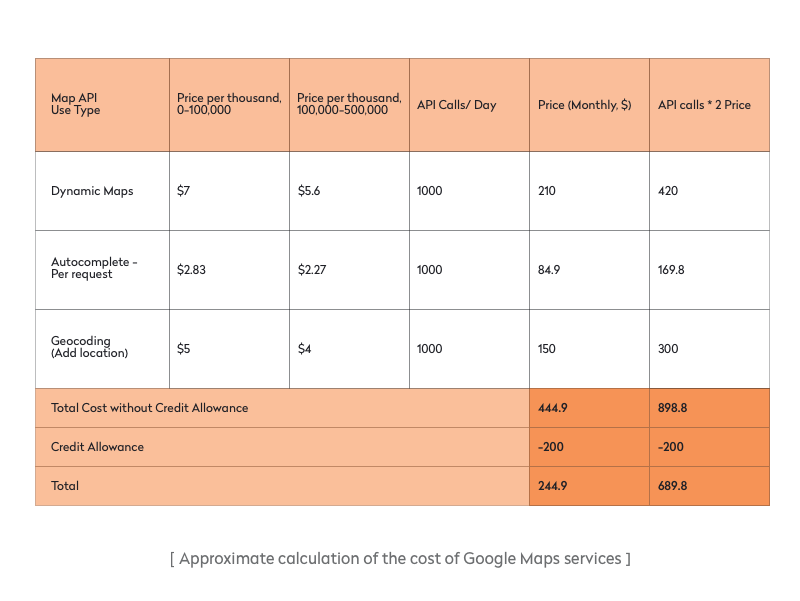
Let’s imagine you have an on-demand delivery business. Your customers have a customer app, where they can find a restaurant near them. Your site’s location pages, which contain maps, are loaded 1,000 times per day (1,000 page loads, not visitors). There are also 1,000 location searches per day using the location auto-completion function. In addition, 1,000 API calls a day are made to add locations.
As a result, you’ll pay Google $245 per month (calculating for a 30-day period). If your traffic doubles, you’ll pay $690, and if it goes up tenfold, you’ll pay $3,361. And that’s only one part of the functionality. You should also enable automatic route planning for couriers and real-time tracking for users, which results in additional expenses.
The good news is that Google provides volume discounts. If you make more than 100,000 monthly requests, you automatically get a 20% discount. If your number of requests surpasses 500,000 monthly, Google offers you to contact a sales manager to discuss individual partnership conditions.
What Google Maps offers to logistics companies
The Google Maps Platform also offers solutions for companies in the logistics, gaming, and retail industries. In particular, the Google Maps API offers the set of tools to integrate for asset tracking and on-demand delivery.
For asset tracking, Google has combined the best functionality from its products to create a convenient solution for companies that need to plan complex routes, locate assets precisely and frequently, manage and operate thousands of assets at scale, or understand real-time road conditions. Components of Google Asset Tracking include:
-
Geolocation — Shows the precise location of indoor and outdoor devices and assets; uses Wi-Fi and cell tower signals to determine the location
-
Geocoding — Converts addresses to geographic coordinates, or vice versa
-
Distance Matrix — Calculates the distance and time for a route
-
Directions — Lets logistics agents calculate current or future travel times based on real-time traffic (Users can create routes with up to 25 waypoints.)
You’ll need to discuss the price of this solution with a sales representative.
Pros and cons of using Mapbox
Mapbox is a rapidly growing location data service that offers various mapping tools for web developers as well as for mobile ones. According to its website, the company boasts 420 million active monthly users and ensures stable support for over five billion requests per day, including from giants like Facebook and Adobe. But what about the main advantages of Mapbox over Google Maps?
Pros
-
Unique customization options. Mapbox reviews show that Mapbox more customizable than Google Maps. While lots of mapping systems offer a finished map, Mapbox is like a box of Legos that developers can put together however they like. Mapbox allows you to create a map style that conforms to your company’s branding. Developers can set the fonts and color scheme and add functionality such as turn-by-turn directions and terrain information. This tutorial will teach you how to create custom maps.
-
Open-source SDKs. Mapbox Maps SDKs are open-source. Mapbox shares their code on GitHub so it can always be seen, analyzed, and improved. Many talented developers actively contribute to the code base. Mapbox Maps SDKs are based on Mapbox GL Native. This library allows you to embed interactive, customizable vector maps into native apps on multiple platforms. You can check out the tutorials for iOS, Android, and web for more information.
-
Integration with PubNub. Mapbox partners with PubNub, which offers infrastructure-as-a-service for live data streaming, builds dynamic map visualizations from real-time data, and incorporates functionality like asset tracking, geocoding, and heatmaps.
-
Mapbox AR. The Mapbox Maps SDK for Unity allows for building location-based service using points of interest (POIs) all over the world. You can add locations using drag-and-drop maps and POIs, 3D buildings and terrain, place-based AR, and more.
-
Offline maps. There’s no offline mode with the Google Maps API. More precisely, offline mode is available in the branded Google Maps app; however, it’s limited to the app itself and isn’t available via the API, so it can’t be integrated into other products. Mapbox provides more flexibility regarding its offline mode. Thanks to its use of vector maps, Mapbox supports offline functionality. Applications created with Mapbox mobile SDKs can download maps for selected geographical areas for use when the device doesn’t have network connectivity. In addition, Mapbox mobile SDKs automatically cache tiles and other resources requested during normal use.
Read also: Lighting the Way for Your Customers: How to Create a Location-Aware App
Cons
Relatively weak coverage. There are many places where Google has better coverage than OSM based services. The reason for this is mainly the fact that Google Maps gets continuous updates. In India and Israel, for example, Google Maps will be a better option.
Solutions for logistics
On their website, Mapbox offers dedicated solutions for a list of industries. Mapbox states that its solution is good for last-mile delivery, fleet management, on-demand delivery, and ride-hailing services.
Mapbox solutions provide tools for the following tasks:
-
Route planning
-
Real-time analytics
-
Delivery tracking
-
Dynamic routing and navigation
The service also has detailed instructions on how to create convenient asset tracking software using Mapbox, Pulumi, and AWS.
Comparing the cost of Google Maps and Mapbox
Before Google drove up the price for their Dynamic Maps API from $0.50 to $7.00 per 1,000 loads, Mapbox had been the service with more limited free functionality. However, while Google has reduced their limits, Mapbox still provides up to 50,000 free map loads for web in a month, and every then each 1,000 of map loads will cost you $5.00. This difference in price between Google Maps and Mapbox is causing many people to consider switching to the Mapbox API.
In addition, Mapbox free plan includes (alongside the 50,000 views and 50,000 active users a month) 50 GB of tileset storage and 5 GB of dataset storage.
Both Google and Mapbox have high-volume discounts. Mapbox activates discounts automatically when the volume reaches a certain mark. Google offers automatic discounts in case of 100K API calls, further discounts for more than 500K API calls should be requested by a client.
When choosing between Mapbox and Google Maps, note that you’ll have to consider any costs for developers to implement APIs and customize the maps.
Read also: Writing a Request for Proposal to Your Potential Software Partner
How to choose?
Having read our post, you know that Mapbox is equal to Google Maps in terms of functionality and even has some essential advantages. But does it really suit your business needs? Answering the following three questions will help you make the right decision:
1. What’s the size of my business?
If you’re a small website or app not generating lots of map views – moreover, if you simply have a map embedded in your website as a static object – then don’t worry about the price hike for Google’s services. You aren’t likely to use up the monthly API calls credit. For those building a startup that uses maps heavily, we recommend using Mapbox.
2. What part of the world is my project focused on?
As we’ve mentioned, Google provides much better map coverage compared to Mapbox. But we suggest you check both services before making a choice. For example, Google doesn’t provide driving directions in South Korea. At the same time, AR navigation with live traffic in South Korea is supported by Mapbox.
Google is undoubtedly good, and if your business thirsts for high precision and speedy maps, we have to admit this service is beyond compare. But it’s also true that Google can unexpectedly disappoint you by starting to charge for a previously free feature, which means money losses for your business.
It’s up to you to decide which service to use. If you want to implement routing and mapping functionality in your logistics software but aren’t sure which solution is best for your business, we can help you with choosing the right map integration. We carefully analyze our clients’ business objectives and requirements to come up with the best solutions. If you choose Yalantis as your software development partner, we’ll gladly suggest the map provider that best suits your business needs.
Ten articles before and after
Top Reasons for Cloud Migration and Step-by-Step Instructions
Six Cloud Migration Strategies Based on Yalantis’ Experience
How to Use WebSockets in Go: A Comprehensive Guide
Full List of the Best Android App Development Tools in 2021
How to Choose the Best-Fit Tools for Logistics Software Optimization