One of the most important steps to take when it comes to developing a successful digital software product is to pick the right tech stack. Why? Because creating a product is not just about designing a nice UI and convenient UX; it’s also about designing a stable, secure, and maintainable product that will not only win your customer’s heart but will also allow you to scale your business. Here’s where the right technology may help.
While you, as a business owner, are busy with things like elaborating your business idea, defining your product’s pricing model, and coming up with powerful marketing, deciding on technologies for your new app is something you'll likely leave up to your developers.
Of course, it’s common practice to rely on your development partner’s technology suggestions. If you do, however, you should make sure your partner understands your business needs and takes into account all the important features you’ll be implementing for choosing a technology stack.
At Yalantis, we believe that having a general understanding of the web development stack is a must for a client. It helps us to speak the same technical language and effectively reach your goals. This is why we’ve prepared this article.
Without further ado, let’s explore what a technology stack is and what tools we use at Yalantis to build your web products.
Defining the structure of your web project
You might have guessed that a technology stack is a combination of software tools and programming languages that are used to bring your web or mobile app to life. Roughly speaking, web and mobile apps consist of a frontend and backend, which are the client-facing application and a hidden part that’s on the server, respectively.
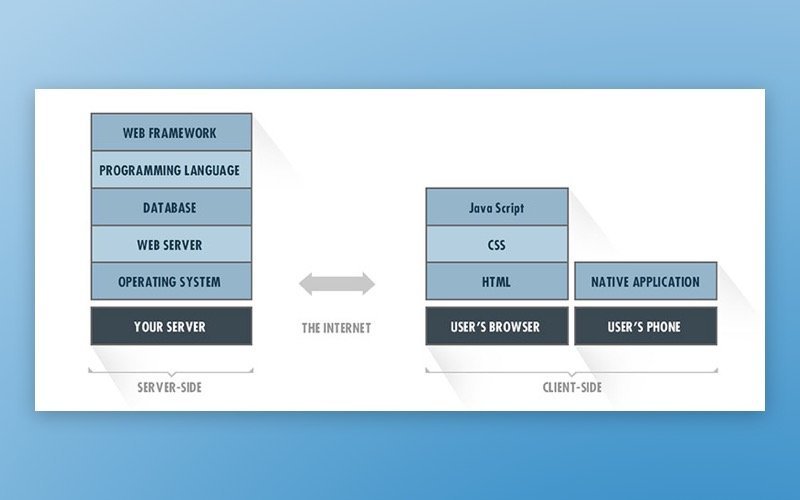
[A typical app tech stack]
Each layer of the app is built atop the one below, forming a stack. This makes web stack technologies heavily dependent on each other. The image above shows the main building blocks of a typical technology stack; however, there may be other supporting elements involved. Let’s view the standard elements of front-end and back-end development in more detail.
Frontend
The frontend is also known as the client side, as users see and interact with this part of an app. For a web app, this interaction is carried out in a web browser and is possible thanks to a number of programming tools. Client-facing web apps are usually built using a combination of JavaScript, HTML, and CSS. We’ll explain the components of the front-end technology stack below.
Tools we use for frontend web development
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is a programming language used for describing the structure of information presented on a web page. Yalantis uses the latest version of HTML — HTML5 — which has new elements and attributes for creating web apps more easily and effectively. The main advantage that HTML5 is that it has audio and video support, which wasn’t included in previous versions of HTML.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a style sheet language that describes the look and formatting of a document written in HTML. CSS is used for annotating text and embed tags in styled electronic documents.
At Yalantis, we use CSS3 (the latest working version of CSS) along with HTML5. Unlike earlier versions of CSS, CSS3 supports responsive design, allowing website elements to respond differently when viewed on devices of different sizes. CSS3 is also split into lots of individual modules, both enhancing its functionality and making it simpler to work with. In addition, animations and 3D transformations work better in CSS3.
JavaScript (or simply JS) is the third main technology for building the frontend of a web app. JavaScript is commonly used for creating dynamic and interactive web pages. In other words, it enables simple and complex web animations, which greatly contribute to a positive user experience. Check out our article on using web animations to create user-friendly apps for more on this topic. JavaScript is also actively used in many non-browser environments, including on web servers and in databases.
TypeScript is a JavaScript superset that we often include in our frontend toolkit. TypeScript enables both a dynamic approach to programming and proper code structuring thanks to the use of type checking. This makes it a perfect fit for developing complex, multi-tier projects.
Frontend frameworks
Frontend frameworks are packages with prewritten, standardized code structured in files and folders. They provide developers with a foundation of pretested, functional code to build on along with the ability to change the final design. Frameworks help developers save time as they don’t need to write every single line of code from scratch. Yalantis has chosen React for frontend web development, as this JavaScript library is perfect for building user interfaces. We also have mastered Angular and use it if a client prefers.
Backend
Even though the backend performs offstage and is not visible to users, it’s the engine that drives your app and implements its logic. The web server, which is part of the backend, accepts requests from a browser, processes these requests according to a certain logic, turns to the database if needed, and sends back the relevant content. The backend consists of a database, a server app, and the server itself. Let’s look at each component of the back-end technology stack in detail.
Backend app
Running on the server, the server app listens for requests, retrieves information from the database, and sends responses. Server apps can be written in different server-side languages depending on the project complexity. Yalantis uses two server-side programming languages: Ruby and Golang. Both of these languages are versatile and boast a list of indisputable benefits. Ruby provides good support for data validation, libraries for authentication and user management, and more. You can explore the various benefits Golang provides in our article on why we use Golang.
We also use Node.js, which is a JavaScript runtime environment. Node.js is commonly applied to the backend and full-cycle development. It has many ready-made solutions for nearly all development challenges, reducing the time for developing custom web applications. Read our detailed comparison of Node.js and Golang to familiarize yourself with the differences between them in terms of scalability, performance, error handling, and other criteria.
Web frameworks greatly simplify backend development, and which you should choose depends on the programming languages you’ve picked. Any programming language has at least one universal framework. Libraries for a framework provide reusable bundles written in the language of the framework: for instance, code for a drop-down menu.
However, frameworks aren’t just about the code: they’re completely layered workflow environments. Yalantis uses Ruby on Rails as a Ruby framework and Gorilla as a Golang framework. Both ensure clean syntax, rapid development, and stability.
Databases
A database is an organized collection of information. Databases typically include aggregations of data records or files. For example, in e-commerce development, these records or files will be sales transactions, product catalogs and inventories, and customer profiles.
There are many types of databases. In this article, we only touch upon databases Yalantis works with to outline some use cases for particular databases. Our specialists work with the following databases and choose which to use depending on the particularities of a client’s project.
PostgreSQL. This database is especially suitable for financial, manufacturing, research, and scientific projects, as PostgreSQL has excellent analytical capabilities and boasts a powerful SQL engine, which makes processing large amounts of data easy and smooth.
MySQL. Especially designed for web development, MySQL provides high performance and scalability. This database is the best fit for apps that rely heavily on multi-row transactions, such as a typical banking app. Generally speaking, MySQL is still a great choice for a wide range of apps.
MongoDB. This database boasts numerous capabilities, such as a document-based data model. MongoDB is a great choice when it comes to calculating distances and figuring out geospatial information about customers, as this database has specific geospatial features. It’s also good as part of technology stack for e-commerce, event, and gaming apps.
Redis. Redis provides sub-millisecond response times, allowing millions of requests a second. This high speed is essential for real-time apps, including for advertising, healthcare, and IoT.
Elasticsearch. This document-based data storage and retrieval tool is tailored to storing and rapidly retrieving information. Elasticsearch should be used for facilitating the user experience with quicker search results.
If you’re interested in a more detailed description of databases and criteria for choosing the most suitable database, read this article.
Application Programming Interfaces
An Application Programming Interface (API) provides a connection between the server and the client. APIs also help a server pull data from and transfer data to a database.
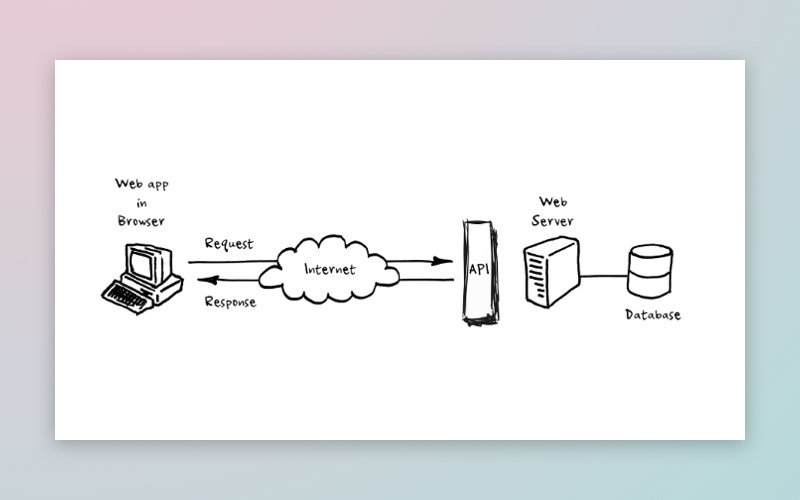
[The web as a client–server app framework]
Numerous services we use daily rely on a huge number of interconnected APIs. If even one of them fails, the service will not function. In order to avoid this, APIs should be thoroughly tested. Our article on API testing can give you a picture of how this is done.
Server architecture
A developer needs a place to lay out written code right from the early days of development. For this, we use a server setup.
There are many variations of server architectures, including those in which the entire environment resides on a single server and those with a database management system (DBMS) separated from the rest of the environment. Your choice of server architecture should depend on such factors as performance, scalability, availability, reliability, cost, and ease of management.
When it comes to the server setup, Yalantis has DevOps specialists to help out. Yalantis provides DevOps as a managed service for companies that run apps in the cloud, as this practice ensures the speed of development and operations.
Yalantis uses the services of cloud providers to host our web applications. We primarily use AWS for hosting web projects due to its flexibility, reliability, and security. As an alternative to AWS, we also use Google Cloud Platform Services, Microsoft Azure, and Heroku. You can compare all the hosting services we use in our post on types of hosting solutions.
A cloud provider gives us a server to use, and then our DevOps specialist sets up the environment — all additional software — to ensure smooth operation of the app. Our DevOps specialists typically use Nginx, which is a powerful web server. Nginx allows for setting up reverse proxies, load balancing, and more.
A DevOps specialist is responsible not only for server setup. They also set up a continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipeline from scratch. Continuous integration makes possible continuous development, adding code, and synchronous testing. Continuous deployment is accountable for delivering code to the server.
We use such tools as GitLab and GitLab for CI/CD. GitLab is a single app for the whole DevOps lifecycle in which all written code is stored. We also use the GitLab CI (Continuous Integration) service, which creates and tests software whenever a developer pushes code to the repository.
Having studied the basics of the technology stack, let’s move on to the criteria that will help you and your development team select the most appropriate technologies for your project.
What to consider when choosing a tech stack
Keep in mind that the type of app you’re developing influences the technology you should select. A medical app, for example, will require high security, while audio/video streaming and file sharing apps will need programming languages and frameworks that can handle high load.
While deciding on the components of the tech stack, also analyze your web app based on the criteria mentioned below to narrow down the options. Keep in mind that web development technologies can be used in different combinations, and frameworks are only to be chosen after the programming language has been agreed on.
Project size
All projects can be classified depending on their complexity, which will affect the choice of technology stack. As the size of a project grows, the complexity of the project usually increases too, as shown in the diagram below:
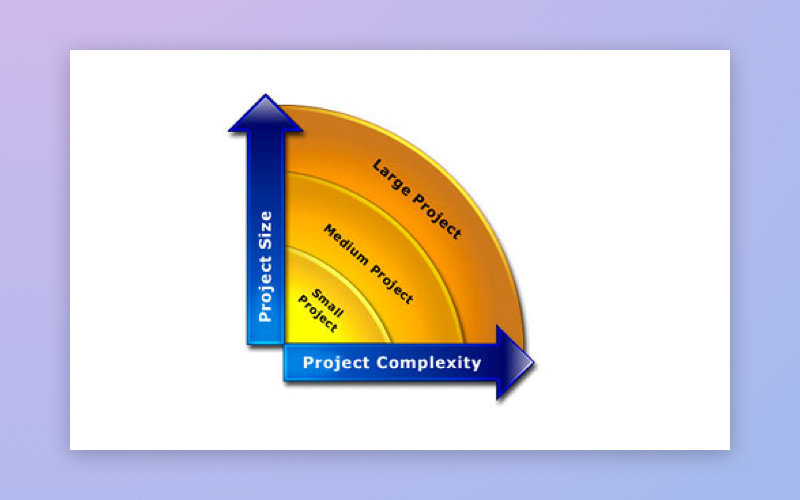
[The dependence between project complexity and size]
Classify your project according to these three categories:
Small projects. Single page sites, portfolios, presentations, digital magazines, and other small web solutions can be implemented with the help of design tools like Readymag and Webflow.
Medium-sized projects. Online stores, financial, and enterprise apps require a more complex stack with several layers and a combination of languages, as these apps have more features and are developed with the help of frameworks. You should also consider cross-platform integrations, as medium-sized projects typically involve multiple systems. For example, there may be a connection between a web app and a company’s backend systems.
Large projects. Social networks and marketplaces are considered large projects, and may require much more scalability, speed, and serviceability. First, identify the features you need to implement. Then prepare a list of relevant questions to ask your development partner to understand if their technology and solutions fully support your idea. You may also analyze other similar solutions on the market and technologies they’ve used so as not to reinvent the wheel. This kind of project development usually involves a complex combination of instruments, languages, and technologies to build individual parts of the app. Deciding on a tech stack for a complex project requires consideration of both functional and non-functional requirements.
Time to market
When your product needs to be developed and launched as soon as possible, you may consider starting with a minimum viable product, or MVP. If you do, we recommend using ready-made solutions that help to minimize the time spent preparing to enter the market. For example, the Ruby on Rails framework, which provides access to a set of basic libraries, will save significant time. There’s a gem available in the RubyGems repository for practically any feature you may want to implement. And if there isn’t, it’s easy to find an expert in the Ruby community who can create the feature quickly.
Third-party integrations will help to add functionality without writing it from scratch. Sticking to a popular technology will also save time on seeking out developers. And to top it all off, well-documented technologies facilitate the development of some features.
Scalability
If you plan for rapid growth, don’t forget that the tools you choose for your tech stack might not have the potential to scale sufficiently. You can scale either vertically, adding additional software for new tasks, or horizontally, adding processing units or physical machines to your server or database. React, Node.js, Golang, and Ruby on Rails have excellent scalability. Your app will also scale well on AWS, as it uses advanced Ethernet networking technology designed for scale along with high availability and security.
Security
Your app may require high security. For instance, if you’re developing a health app, be careful when choosing technologies as many are not secure enough. Ruby on Rails, however, will be a good choice as it provides DSL (Digital Subscriber Line), helping you configure a content security policy for your app.
To provide security for the medical web app Healthfully, our specialists ensured the following:
-
All interactions with the app are carried out using an API.
-
Access to the API is token-based, with a limited time of token validity.
-
Access authorization is carried out for each request.
-
All infrastructure is in AWS, and access from the internet is possible only to the API; all other communication is behind the firewall.
-
Backups are performed on a regular basis.
-
We did not have to make the product HIPAA compliant, but our developers were ready to meet HIPAA Compliance.
[Components of the eCuris app]
How not to lose a fortune developing a web app
The following tips will help you be prepared for web app development so as not to have regrets about outsized expenses you could have avoided.
Make sure your specification is clear and understandable. If you outsource your project to a offshore web development team, make sure you have a clear project specification to help your developers prepare a precise estimate, which will allow you to plan your expenses. Any ambiguity will lead to a higher price. A detailed specification will allow you to avoid this risk.
Create an MVP first and then test it. Keep in mind that in certain cases a landing page can serve as an excellent and inexpensive MVP. Make sure your product will be in demand and consider all the errors that occur while testing. Only then should you develop a complete solution.
Use ready-made solutions when possible. Keep in mind that you don’t have to build all features from scratch, as similar solutions may already exist in the form of community-built libraries or third-party integrations (registration via Facebook or Google, for example). We’ve already mentioned that Ruby on Rails offers many libraries that accelerate web app and website development. ActiveAdmin is one of them. Using ActiveAdmin, developers can enable powerful content management functionality for their web apps.
Save on cloud hosting solutions. We use Amazon Web Services as the primary service for hosting web projects we create. AWS offers flexible pricing, with each service priced a la carte. This means you pay only for the services you use. This makes a lot of sense for server infrastructure, as traffic is unpredictable. This is especially true for startups as it’s hard to say when exactly they’ll attract the first wave of users. That’s why this pricing model suits startups best.
Think in advance. When selecting technologies for your web app, think about how you’ll support the app in the long run. Support will be easier if the app has a good architecture and optimized code from the very beginning. Any unsolved problems will appear later on and cause even worse problems. Support and maintenance should be considered when choosing the tech stack, as their consideration will simplify updates even if you decide to change software development service providers.
There are the most widely discussed web application development trends in 2021. Artificial intelligence is gaining ground, as it offers a personalized user experience by gathering users’ data and speeds up interactions with a web application. Another trend that’s worth mentioning is progressive web apps (PWAs), which provide a mobile-like experience and can be easily installed via a sharable link.
Different web apps use different development tools. This is the best evidence that there’s no one most effective technology stack. When choosing a technology stack for Web application development, keep in mind the specifics of your project. Solution architects at our outsourcing company consider your product requirements and turn them into an architecture and design that lay the foundation for a top-notch solution. Our agency can help you with this if you share your web app idea and expectations with us. Tell us what you want to achieve, and our technical experts will gladly suggest the best tools to make it happen.
Ten articles before and after
Practical Tips on Adding Push Notifications to iOS or Android Apps
How to Create a Restful API: Your Guide to Making a Developer-Friendly API
How to Use GitLab Merge Requests for Code Review
How to Speed Up JSON Encoding and Decoding in Golang
How to Deploy Amin Panel Using QOR Golang SDK: Full Guide With Code
Which Payment Gateway Integration to Choose for Your App
How to Load Test an API to Ensure Your App Works Smoothly
Golang and Node.js Comparison: Scalability, Performance, and Tools
Real-Time Features: Best Use Cases and Reason To Implement Them In Your App